Link to article here
Under the surface, a very different Hong Kong story
BYMICHAEL EDESESS9 HOURS AGO
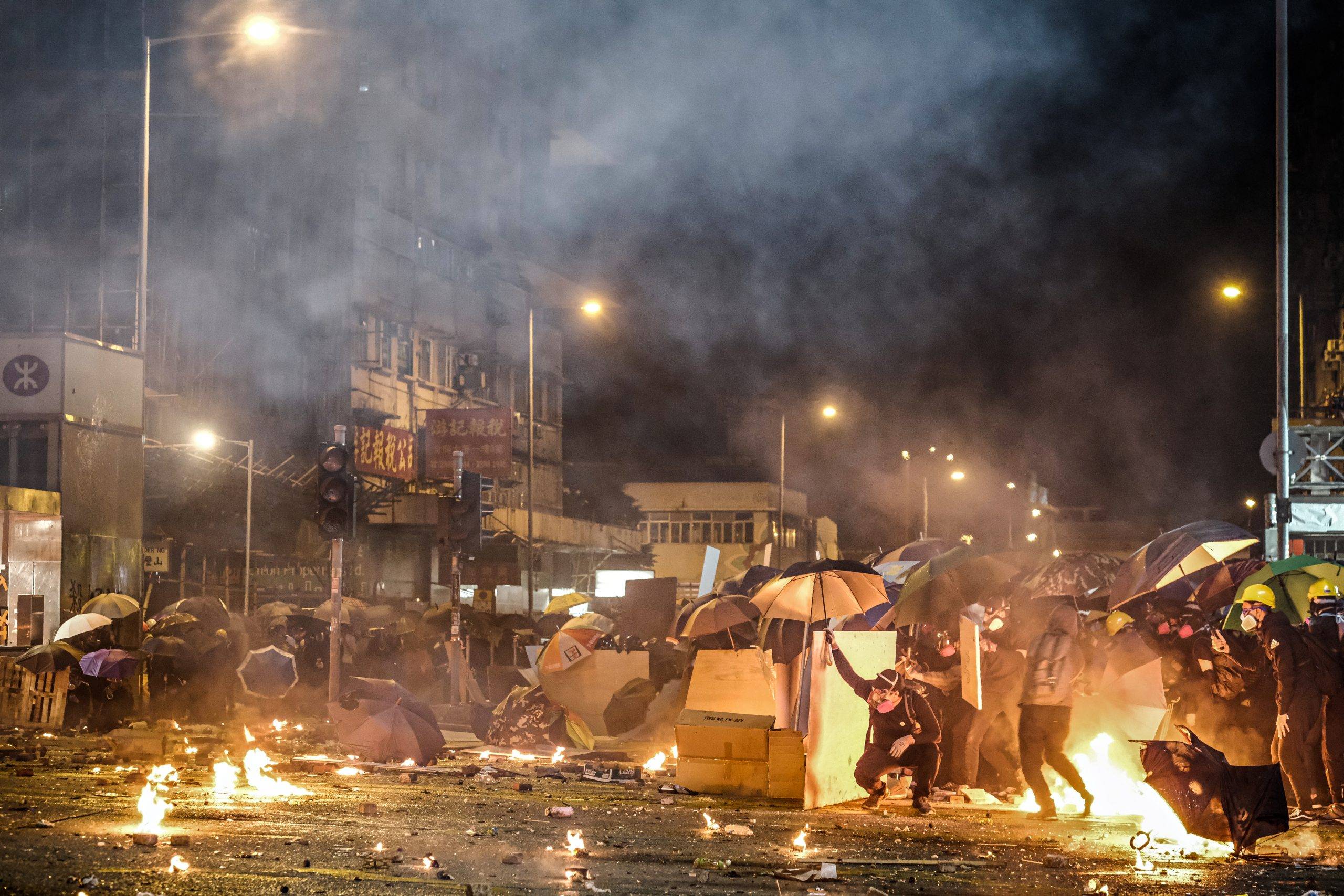
- The widely reported narrative that Beijing tried to impose a law to snatch dissidents from Hong Kong in 2019 was never true
- Peaceful demonstrators quickly fled the protests as they realized something dark, violent, and well-organized lay just below the surface
- The media simply relayed stories and numbers they were given by one side, failing to do their jobs to investigate and report
- The allegation that “police brutality” was the issue was simply false: Hong Kong is a low-crime city with good relations between citizens and law enforcement
THERE ARE TWO STORIES about what happened in Hong Kong in 2019.
One, portrayed in Western media, says Beijing broke its “one country, two systems” promise and encroached on the freedoms of Hongkongers, who bravely responded with massive pro-democracy protests that were met with police brutality.
The other says that organizers of violent riots were funded by the U.S. to pay rioters and special consultants who taught them how to make the compliant Western press write that they were pro-democracy protesters fighting against repression and police brutality.
Guess which one is true.
EYEWITNESS EVIDENCE
Unlike the multitude of offshore armchair commentators expressing their views on the violent social upheaval that began in June 2019, I lived in Hong Kong through that period, as did Nury Vittachi, whose eyewitness investigative journalism I will discuss.
We each saw, directly, what was happening.
NEW YORK TIMES FEATURE
On October 14, 2014, an op-ed was published in The New York Times titled, “Hong Kong’s Pop Culture of Protest,” by Vittachi, a Sri Lanka-born journalist living and writing in Hong Kong since 1987.
The op-ed celebrated the protest known as the “Umbrella Movement” that was under way in Hong Kong at the time. Vittachi explained that the protest was about “rejecting the influence of Beijing over Hong Kong’s next election.”
I visited the central site of that protest at that time, and I, too, felt the celebratory atmosphere. Protests in two of the busiest areas of Hong Kong, the business district known as Central, and Nathan Road, the main thoroughfare in the Mongkok district, had filled the streets and brought traffic to a standstill. The double-decker buses that traverse Nathan Road, near where I lived – as many as hundreds per hour – had found ways around the blockages and were otherwise carrying on as usual, as if they were genially accommodating the protests.
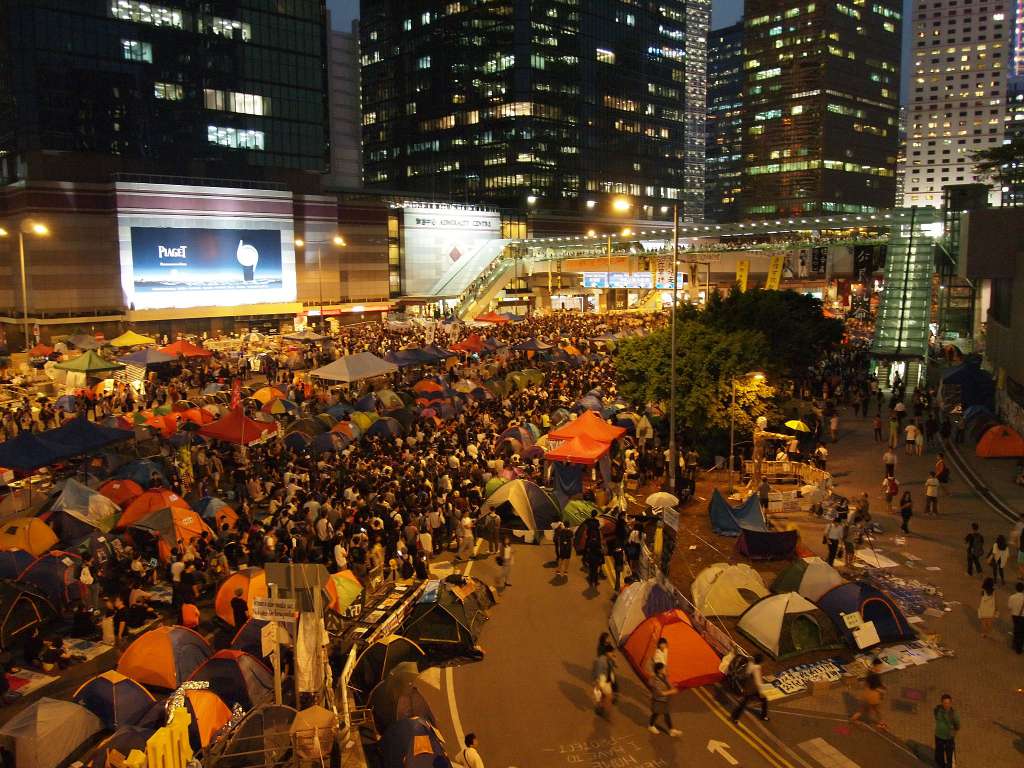

When I visited the protest site in Central, I marvelled at its vast expanse of colourful upscale tents, of the type you find at Patagonia. They were shelters for the huge number of protesters camped out there.
My first thought was, “When this is over, perhaps the city planners will realize what a boon to the city it would be to turn this downtown area into a pedestrian mall.”
I also thought for a brief moment, “I wonder how they pay for all these tents? They aren’t cheap.” Hong Kong is a rich city, though most of its residents aren’t.
CONFUSED MESSAGE

Another thought that occurred to me was that if someone didn’t know who the leader of this movement was, they would think it was John Lennon, because his picture was everywhere and his song, “Imagine,” filled the air.
This was curious because the protests were presumably anti-Communist, but Lennon himself described the song as “virtually the Communist Manifesto,” with its dreams of ending private property and religion.
THE BACKGROUND
In 1842, Hong Kong island was seized by force during the Opium War from China by Britain. Additional territory was added to the city later, with the largest part area-wise, the New Territories, being annexed in 1898 by a 99-year gunboat-lease agreement with China. Therefore, it seemed appropriate to China to request the entire city back at the end of that lease in 1997.
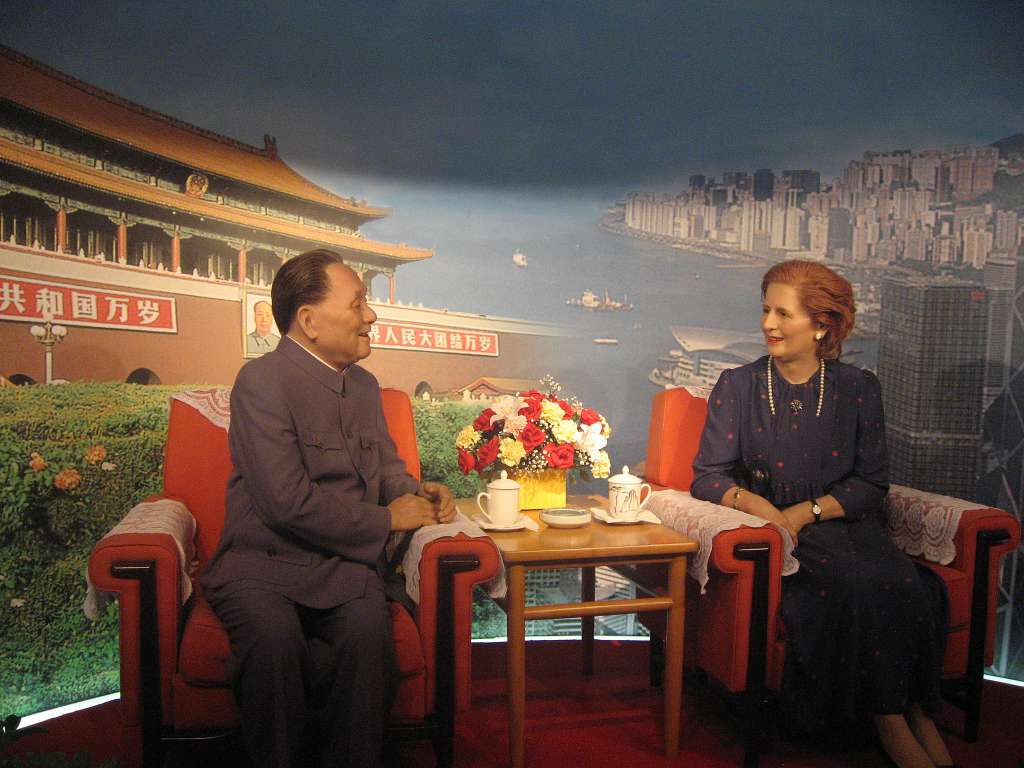

An agreement was struck in the Sino-British Joint Declaration in 1984 for the territory to be handed back to China in 1997. That event was subsequently called “the handover.”
In the joint declaration, China agreed that Hong Kong would be governed by a doctrine of “one country, two systems,” in which it would keep its form of government, legal systems and policies including its free speech and press traditions for at least 50 years following the handover.
This agreement was to be elaborated in a Hong Kong mini-constitution known as the Basic Law, negotiated by a committee of Hong Kong and mainland China officials.
UNDEMOCRATIC PAST
One provision of the Basic Law was that Hong Kong’s chief executive – its top official – would be elected by universal suffrage, something that had never happened when the British were in charge. Although 92% of Hong Kong’s population are Chinese, the chief executive under the British was an unelected British official appointed by the Queen.
The actual wording of the provision is as follows:
- “The method for selecting the Chief Executive shall be specified in the light of the actual situation in the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and in accordance with the principle of gradual and orderly progress. The ultimate aim is the selection of the Chief Executive by universal suffrage upon nomination by a broadly representative nominating committee in accordance with democratic procedures.”
Hongkongers had agitated after the handover for realization of that provision. In August 2014 Hong Kong’s civil service finally promulgated a process by which the chief executive would be elected. The election would be by universal suffrage, but the nominees would be screened and vetted by a 1,200-strong committee of Hongkongers, much the same committee that had been electing the chief executive since the handover. The majority of that committee were representatives of Hong Kong business communities. Since they did a lot of business with the mainland, it was believed – generally correctly – that they tended to have mainland sympathies, or to be “pro-Beijing.”
UNIVERSAL SUFFRAGE REJECTED
Many Hongkongers who had been participating in peaceful pro-democracy protests over the years – including Vittachi – interpreted this as a failure to adhere to the promise of free elections, though it was definitely not in violation of the Basic Law’s actual wording. Vittachi, a widely-read journalist in Hong Kong, gave rise to a viral meme by saying that the proposal to vet the nominees amounted to a “choose your own puppet” election.
The pan-democrats – the pro-democracy faction – rejected the offer.
The unfortunate result, from Hong Kong’s perspective – and from everybody else’s, it turns out – was that the chief executive continued to be elected by that 1,200-strong committee, not by universal suffrage.

NEED FOR EXTRADITION LAW
Hong Kong was behind other jurisdictions in the passing of an extradition law recommended by the United Nations Model Treaty on Extradition, which “urges all States to strengthen further international co-operation in criminal justice” and “urges Member States to inform the Secretary-General periodically of efforts undertaken to establish extradition arrangements.”
Most jurisdictions worldwide had extradition treaties with most other jurisdictions worldwide, but Hong Kong had few.
As Vittachi noted, “Britain had signed extradition treaties with numerous countries with utterly abysmal human rights records, such as Iraq and Zimbabwe. America had signed deals with the Congo, Myanmar and El Salvador, among others.”
MURDER MOST FOUL
When a Hong Kong man murdered his pregnant girlfriend during a joint holiday in Taiwan, and then escaped back to Hong Kong, he could not be tried for murder as Hong Kong criminal law does not apply in Taiwan.
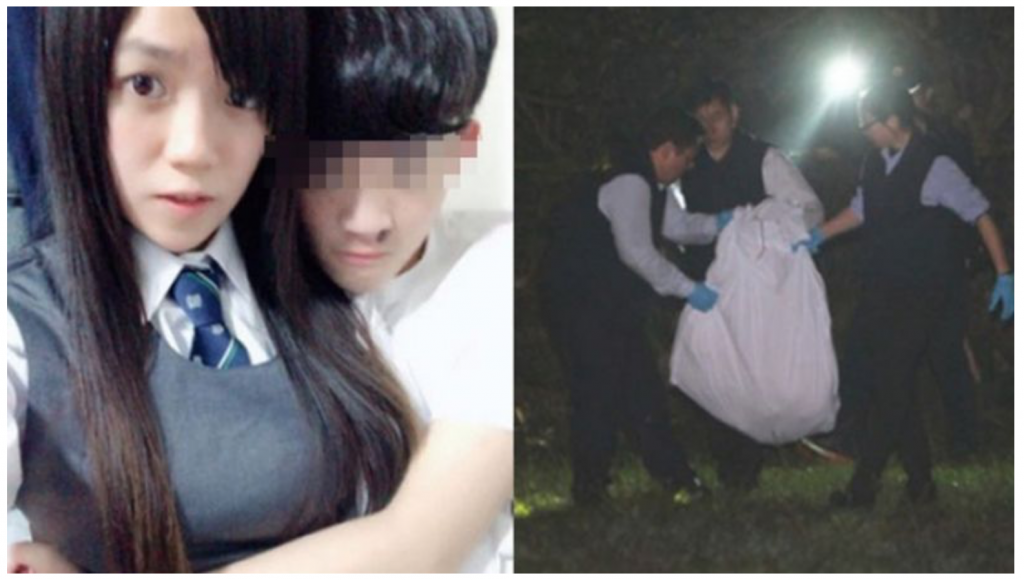

Neither could he be extradited due to that lack of a legal framework. This prompted Hong Kong’s Chief Executive Carrie Lam to take care of unfinished business by proposing an extradition law for Hong Kong in February 2019.
But the Hong Kong protestor inclination was to view this as a way for Beijing to snatch political protestors and try them in the mainland. (This inclination was fuelled by the fact that there had been incidents of Hong Kong booksellers who sold books critical of high-level mainland political figures being snatched, though it was not known how this happened or who did it.)
The proposed law would allow nothing of the sort, but it was seen nonetheless as another threat to the one country, two systems model.
SCARE STORIES
As a result, after scare stories about the proposed law had circulated widely, a massive peaceful protest took place on June 9. The protest leaders told the international media that a million people had participated in the march, and the international (i.e., Western) media dutifully printed that without checking. But any systematic count would have revealed that the number of marchers was far less.
It was, nevertheless, a massive turnout. Chief Executive Carrie Lam responded by welcoming the peaceful protest. But after more such protests, she responded to popular sentiment and withdrew the bill.
UTTER CHAOS
In spite of the withdrawal of the bill – to cover the next six months very, very briefly – the protests continued, then descended into utter chaos.
A violent faction became prevalent, commandeering the streets, invading, trashing and desecrating Hong Kong’s legislature (called Legco), hurling petrol bombs and bricks pried loose from Hong Kong’s streets at police and eventually shooting arrows, some flaming, and launching the bricks and bombs using catapults.
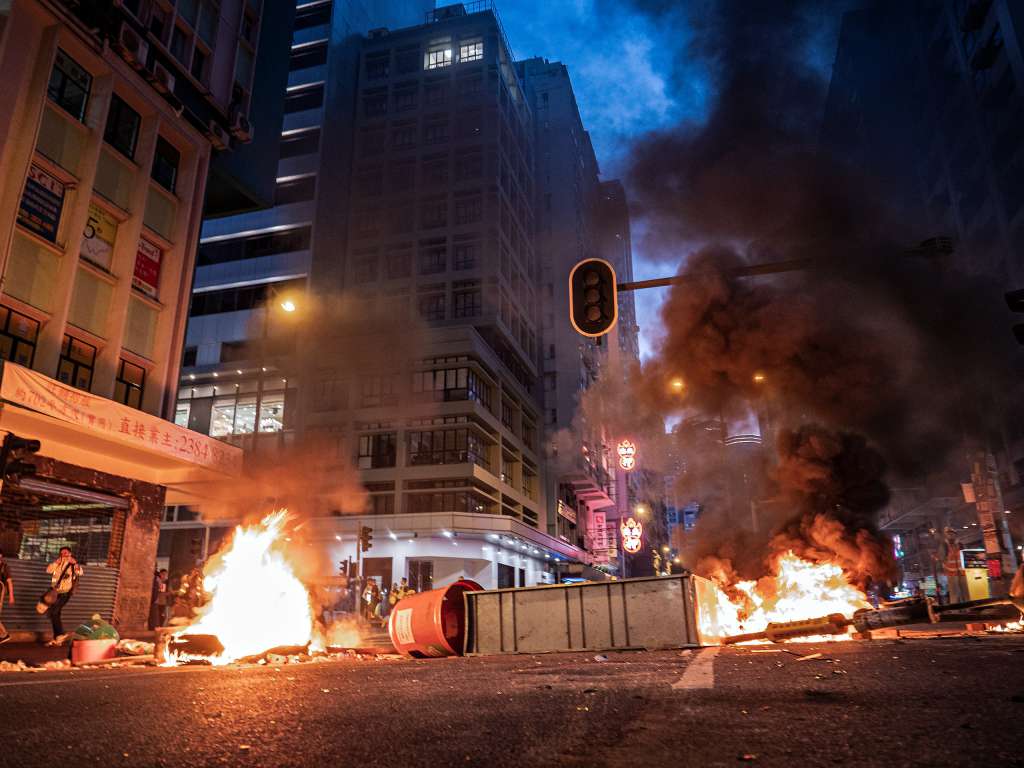

The protestors swarmed into Hong Kong’s metro stations and broke everything they could. They demolished Hong Kong’s world-class malls and stores and businesses that had any perceived relationships to mainland people or even to Mandarin speakers (Hong Kong’s spoken language is Cantonese while Mandarin is spoken on the mainland).
They killed one innocent bystander, set another on fire and beat up many who disagreed with them. They wounded many police officers, some severely.
In the end, they took over two university campuses, where they occupied bridges over heavily trafficked highways and threw large objects down on the traffic, set up weapons manufacturing stations, and battled police.
POLICE BLAMED
The rioters blamed the police, claiming “police brutality.” They spread rumors that police had killed a number of protestors, perhaps thousands.
Through all this, the Western press continued to call the riots “pro-democracy protests,” and the cause of those protests suppression by Beijing.
The much larger group of peaceful protesters drifted away from the demonstrations and no longer participated. Most of the erstwhile leaders of that group, called the pan-dems or pan-democrats, did not roundly condemn the rioters, not even when they presented their absurd “five demands, not one less!” which included the non-negotiable demands that they all be granted amnesty and that their protests not be called riots.
One of Vittachi’s readers made the Dave Barry-like comment: “They are literally rioting to protest against being defined as rioters,” he said, amazed. “You can’t make this stuff up.”

SCALES FALL FROM OUR EYES
In his book, “The Other Side of the Story: A Secret War in Hong Kong,” published in December 2020, Vittachi explained what happened.
Anyone with an interest in what has been happening in Hong Kong should read it, whether they have the least predisposition to agree with it or not.
Although nearly everybody in the United States will vehemently deny this, and say that it is propaganda from Beijing, it is obvious that it has much more than a grain of truth in it.
It is the truth.
PETROL BOMB TRAINING
Vittachi, in his role as a peripatetic journalist in Hong Kong for over 30 years, has cultivated a large number of followers and contacts, many of whom send him emails and messages and serve as his extended eyes and ears.
These people include financial executives as well as ordinary Hong Kong wives and mothers, students, and other contacts. Vittachi maintains “offices” at various coffee shops around the city where he meets with people to chat and get local opinions and observations.
He teaches courses at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, the largest university in the city and was able to visit it during the last and final and most intense battle in November 2019, when the rioters occupied the campus and were surrounded by police.

There, he says, “I watched men train younger people how to do a long run-up and then release their missiles at ‘about 42 degrees’ so that they flew in a graceful curving arc, smashing into a pillar in the distance. In another area, masked archers were practicing the use of high-technology bow and arrow sets. Over in the swimming pool area, men were experimenting with different substances for Molotov cocktails to see which spread the furthest and burned for the longest period.”
THE REAL STORY
His network of ordinary Hongkongers and informers at high levels brought him the real story. The protestors were neither students nor at the universities but hired rioters.
When the occupiers of Hong Kong Polytechnic University finally gave up and filed out and surrendered to the police, it was found that of about 1,600 occupiers, only 46 had any relation to the university.
CASH WAS FLOWING
“Adults, youths, school children, and even domestic helpers have told me that they have been offered cash in significant amounts – sometimes thousands of Hong Kong dollars – to join the protests. Teachers tell me children from their schools, kids who were clearly under 18, were offered HK$300 each (that’s about US$40) to bulk up the numbers at protests. They just needed to turn up in black and do some shouting, throw a few bricks and that sort of thing.”
Who was paying them? “This year alone,” says Vittachi, “the U.S. has budgeted $643,000 (HK$5 million) for pro-U.S. anti-China activists in Hong Kong through the National Endowment for Democracy (NED), the CIA’s regime-change arm – but other large sums are being sent through other groups. These include the Open Technology Fund, which presents itself on its website as a non-profit independent organization but is a U.S. government-led operation to boost protester organizations’ communications capabilities.”
REVOLUTION CONSULTANTS
You don’t believe this? But it should be obvious. The United States has been funding government destabilization efforts in many countries for 70 years – and worse. Why should it be different now?
Part of the money was used to pay professional protest consultants, some of them from Serbia who were experienced from their anti-Milosevitch work, to teach protesters how to stage their activities so that journalists and photographers are led to photograph lone protesters being wrestled to the ground by police, feeding allegations of “police brutality.”
THE AFTERMATH
The stories the protesters told the Western media were almost all lies, but the Western media sopped them up.
Police brutality was not the cause of the riots. Police killed no one and harmed very few, considering the level of violence of the rioters. Vittachi noted that “The most recent Police Service Satisfaction Survey at the time was the one taken just last year, in 2018, in which 84% of respondents were either ‘quite satisfied’ or ‘very satisfied’ with the overall service performance of the police. Furthermore, 79% of respondents were either ‘quite confident’ or ‘very confident’ in the police.”

The United States should have such a police force. Referring to the way the story was reported by the Western media, Vittachi says: “Hong Kong police had instantly and miraculously been transformed overnight from one of the best-loved police forces in the world to the most brutal police force in the world.”
RIOTERS HOPED FOR BEIJING TANKS
The Hong Kong police, overwhelmed by the rioters, mostly stood back and let things happen, to preserve order as best they could in a very crowded city with substantial fire hazard from the Molotov cocktails that the rioters were throwing – even in underground MTR stations – and to avoid causing any deaths or serious injuries. Remembering Beijing’s brutal crackdown on protesters at Tiananmen Square in 1989 – an event that was annually commemorated by Hong Kong’s protest movement – there was a fear that Beijing would have to step in to quell the riots, and such a crackdown would occur again.
In fact, that was probably what the rioters – and their U.S.-based handlers – hoped for.
BEIJING’S SURPRISING PATIENCE
But instead, Beijing took a velvet-glove approach. The Hong Kong Basic Law had specified that:
- “The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region shall enact laws on its own to prohibit any act of treason, secession, sedition, subversion against the Central People’s Government, or theft of state secrets, to prohibit foreign political organizations or bodies from conducting political activities in the Region, and to prohibit political organizations or bodies of the Region from establishing ties with foreign political organizations or bodies.”
This would not be much different from security laws in many other countries, including the US, Australia, and numerous others.
But the Hong Kong government had not been able to enact such a law when it tried in 2003 due to the protest movement and suspicion of Beijing. Now, Beijing simply imposed such a law, and the Hong Kong government has been enforcing it strictly, applying it to those persons in Hong Kong who provided encouragement, aid and support to the violent riots and coordinated with foreign powers, most specifically the US.
This may not have been the endgame that anybody wanted, but at least Beijing didn’t crack down violently.
REPORTER’S REGRET
Vittachi now regrets that he didn’t support accepting Beijing’s half-a-loaf offer of democratic election of Hong Kong’s chief executive in 2014. I had written in 2016 that Hong Kong’s democracy seekers needed to go slow, but the recommendation was not taken.
“That was the key moment,” Vittachi says, “when Hong Kong could have moved towards being a Western-style democracy. But we missed it.”
And this is true. With the aid of the United States, Hong Kong was shifted from the path of greater – if not perfect – democracy to the path, at least for the time being, of less democracy.
Thanks a lot for the help.
Vittachi says of his long history of marching for Hong Kong’s “one country, two systems” ideal, “We were marching not against China, but in favor of China being its best self.”

Michael Edesess is an economist and mathematician. An adjunct associate professor and visiting faculty member at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, he is also managing partner and special advisor at M1K LLC, and a research associate of the Edhec-Risk Institute.
This article first appeared in Advisor Perspectives, a US financial on-line publication.















